
Project
Nano-satellite “MicroOrbiter-1” プロジェクトの概要 (Summary of MicroOrbiter-1 project)
MicroOrbiter-1プロジェクトは、2021年創業の民間スタートアップ企業であるマイクロオービター社(本社:東京都千代田区丸の内1-8-2)が超小型衛星打ち上げ実績では世界トップクラスの九州工業大学との共同研究でLoRa通信を使って地上の低電力消費IoTセンサーデータを低軌道周回衛星で収集し地上ユーザーに地球局経由ネットで届ける実験的な衛星開発プロジェクトです。(The MicroOrbiter-1 project is a joint research project by MicroOrbiter Inc. (head office: 1-8-2 Marunouchi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo), a private start-up company founded in 2021, with Kyushu Institute of Technology, a world-leading CubeSat launcher. This is an experimental satellite development project that uses LoRa communication to collect low power consumption IoT sensor data on the ground with a low earth orbit satellite and deliver it to ground users via the earth station.)
本プロジェクトは、九州工業大学にて先行したプロジェクトであるBIRDSシリーズで蓄積されたハードウエア・ソフトウエアの知識継承を行っています。ミッションの概要は以下の通りです。(This project inherits the knowledge of hardware and software accumulated in the BIRDS series, which was a project preceded by Kyushu Institute of Technology. The outline of the mission is as follows.)
■ミッション: 特定小電力無線局からの微弱センサー信号をLoRa変調方式で無線免許不要の920MHzバンドで低軌道衛星で受信しStore&Forward方式で中継 (Mission: Weak sensor signals from specified low-power radio stations are received by a low-orbit satellite in the 920MHz band, which does not require a radio license, using LoRa modulation, and relayed by the Store&Forward method.)
弊社は「身近になる人工衛星、身近になる宇宙空間」をモットーに超小型衛星の企画・開発を目指しその過程で得る知見を糧にし宇宙ビジネスを創造的に発展させるという目的で創立されました。本プロジェクトの遂行によって、超小型衛星開発の技術的なノウハウの獲得のみならず、超小型衛星開発の為の全般的な流れ、国際周波数調整プロセス、衛星通信の為の電波申請の流れ、JAXAとの安全審査のやり取り、宇宙活動法のプロセス、及びロケット打ち上げに関する諸手続きについてノウハウを取得しています。(Our company was founded with the motto of “Familiar with satellites, Familiar with outer space” with the aim of planning and developing CubeSats and using the knowledge gained in the process to creatively develop the space business. Through the execution of this project, we not only acquired technical know-how for microsatellite development, but also the general flow for microsatellite development, the international frequency adjustment process, the radio wave application flow for satellite communication. Also we have acquired know-how on safety review interactions, space activity law processes, and rocket launch procedures.)
世界を見渡すと超小型衛星打ち上げを計画し、また衛星開発の為のキャパシティビルディング能力を欲している海外の国あるいは機関(海外カスタマー)がまだまだ多数あります。弊社は、九州工業大学との戦略的パートナーシップをベースに、MicroOrbiter-1プロジェクトでの経験を活かし海外カスタマーのニーズを取り込むインバウンド事業も促進していきたいと思います。(Looking around the world, there are still many overseas countries or institutions (Overseas Customers) who are planning to launch CubeSats and want capacity building capabilities for satellite development. Based on our strategic partnership with Kyushu Institute of Technology, we would like to utilize our experience in the MicroOrbiter-1 project to promote inbound business that incorporates the needs of overseas customers.)
Nano-satellite “MicroOrbiter-1” プロジェクトの歩み (History of MicroOrbiter-1 project)
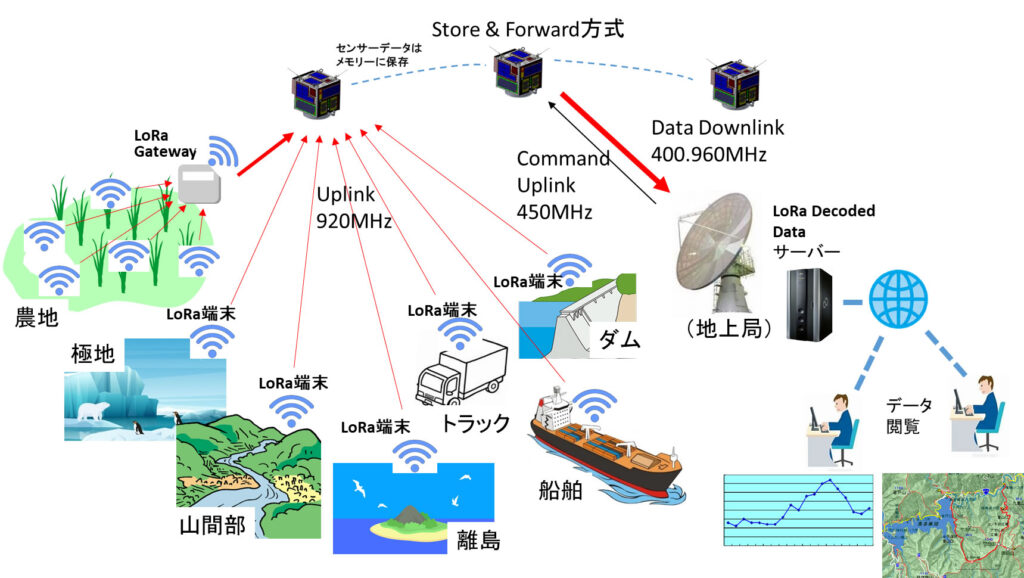
■ Nano-satelliteを使用するLoRa IoT 衛星通信 (LoRa IoT Satellite communication using CubeSat)
低消費電力、長距離通信、広域カバーを特徴とするLPWA(Low Power Wide Area)IoT通信技術を利用し、地球上の任意の場所に設置されたセンサーからの微弱データを拾えるLoRa IoT衛星通信システムを実現させる為に、LPWAの一つの有力な方式であるLoRa方式の低コスト超小型衛星の共同開発を国立大学法人 九州工業大学と進めています。
In order to realize LoRa IoT satellite communication system that uses LPWA IoT communication technology featuring low power consumption, long distance communication, and wide-area coverage, and picks up the weak data from sensor terminals installed anywhere on earth, we are jointly developing a low-cost LoRa IoT micro satellite with Kyushu Institute of Technology.
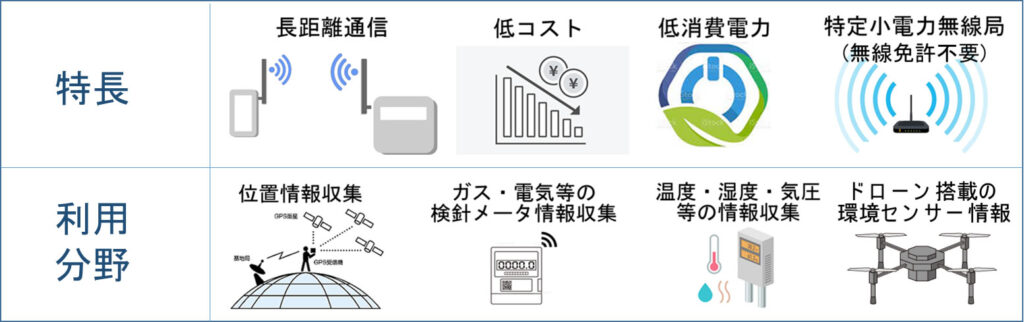
■ LoRa無線通信方式の特徴と利用分野 (Features and application fields of LoRa IoT communication system)
1.長距離通信、低コスト、低消費電力、無線免許が不要な特定小電力無線局
Long-distance communication, low cost, low power consumption, specified low-power radio station that does not require a radio license.
2.位置情報データ収集、ガス・電気等の検針メータ情報収集、温度・湿度・気圧等の情報収集
Location information data collection, gas/electricity meter reading information collection, temperature/humidity/barometric pressure information collection
■ LoRa変調方式によるIoT衛星通信システムのイラスト (Illustration of IoT satellite communication system using LoRa modulation)
■エンジニアリングモデルの開発状況 (Engineering model development status)
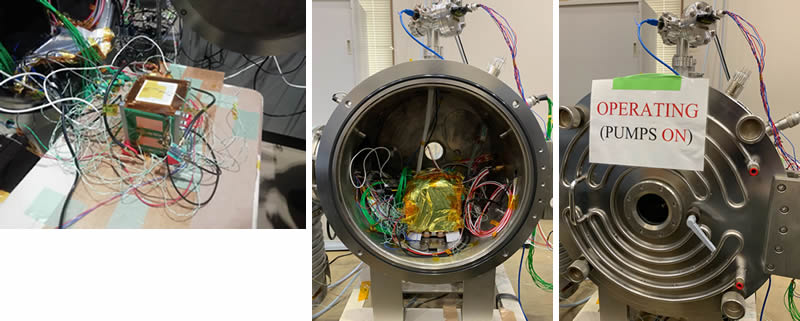
2022年3月31日Critical Design Reviewが終了し、Engineering Model (EM)が姿を現しました。

振動試験、真空熱試験、電波暗室での各種電波試験が成功裏に完了しました。 On March 31, 2022, Critical Design Review was completed, and the Engineering Model (EM) has appeared. Vibration test, vacuum heat test, and radio wave test have been successfully completed.

 写真は組み立てた状態のEngineering Modelです。EM内部のボードにはEMの設計、検査、組み立てに協力したフィリピン、エルサルバドル、イギリス、ブータン、ネパール、イタリア、パラグアイ、ブラジル、トルコ、ジンバブエ、モロッコ、スーダン、スリランカ及び日本の研究者や留学生の名前が刻まれています。Photo shows the assembled Engineering Model. On the board inside the EM are engraved the names of researchers and international students from Philippine, El Salvador, UK, Buhtan, Nepal, Italy, Paraguay, Brazil, Turkey, Zimbabwe, Morocco, Sudan, Sri Lanka and Japan who were involved in the design, inspection, and assembly of the EM.
写真は組み立てた状態のEngineering Modelです。EM内部のボードにはEMの設計、検査、組み立てに協力したフィリピン、エルサルバドル、イギリス、ブータン、ネパール、イタリア、パラグアイ、ブラジル、トルコ、ジンバブエ、モロッコ、スーダン、スリランカ及び日本の研究者や留学生の名前が刻まれています。Photo shows the assembled Engineering Model. On the board inside the EM are engraved the names of researchers and international students from Philippine, El Salvador, UK, Buhtan, Nepal, Italy, Paraguay, Brazil, Turkey, Zimbabwe, Morocco, Sudan, Sri Lanka and Japan who were involved in the design, inspection, and assembly of the EM.
真空熱試験を実施する前のチャンバー内に設置され、衛星の内部機器に計測用ケーブルが取り付けられた状態の衛星の写真です。試験は真空状態で-20℃から+65℃の範囲で24時間連続行われる。These are pictures of the satellite before conducting vacuum thermal test with measuing cables attached to the satellite’s internal boards. Test is performed continuously for 24 hours in the range of -20°C to +65°C under vacuum.
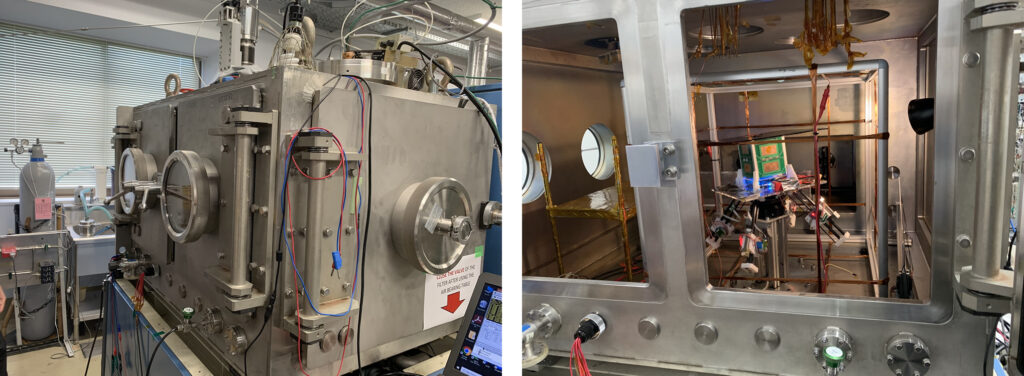
振動試験台にエンジニアリングモデルが設置された写真(左)、超小型衛星との通信を行うための地上無線設備の写真(中)、衛星の各種電波実験の為の電波暗室(Anechoic Chamber)の写真(右)。
A photo of an Engineering Model installed on a vibration test bench (left), a photo of terrestrial radio equipment for communicating with satellite (middle), a photo of an anechoic chamber for satellite radio experiment (right)

当社超小型衛星の姿勢制御は地磁気を利用したPassive Magnetic Attitude Control System(沿磁力線姿勢制御方式)です。この方式で衛星の回転の安定化の為にヒステリシスダンパーを使用しますがそのダンパー特性を評価する為の実験装置がありその写真を掲載します。(2022年7月)
Attitude control of our micro satellite is based on the Passive Magnetic Attitude Control System (attitude control system along magnetic lines of force) that uses geomagnetism. In this method, a hysteresis damper is used to stabilize the rotation of the satellite, and there is an experimental device for evaluating the damper characteristics, photo of which is showm here. (2022-July)
■フライトモデルの開発状況 (Flight model development status)
衛星のFlight Modelをクリーンルームで組み立てるための準備が進んでいます。(2022年7月)
Preparations are underway to assemble the satellite Flight Model in a clean room. (2022-July)


衛星本体及び地上通信装置に対する無線局予備免許通知書を受け取りました。またその後に実施される衛星本体の検査が九州総合通信局検査官により九州工業大学内のクリーンルーム内で実施され、申請書の各種パラメータを現場で検証し問題ないことを確認し無事検査パスしました。(2022年9月)
We received the radio station preliminary license notification for the satellite body and ground communication equipment. After that, the inspection of the satellite was carried out by inspectors from the Kyushu Bureau of Telecommunications in the clean room of the Kyushu Institute of Technology. Various parameters of the application form were verified on-site, and it was confirmed that there were no problems, and the inspection successfully passed. (2022-Sept)

当社衛星は米国のロケットで打ち上げられISS(国際宇宙ステーション)まで運ばれ、ISSから宇宙に放出されます。ISSから放出の時に使用されるPODに当社衛星がスムーズに入り、放出できるかどうかのフィットチェックを行う事になっていますのでJAXAからお借りしているPODでチェックを行い、問題無い事が確認できました。(2022年11月)
Our satellite will be launched by US rocket and transported to the ISS (International Space Station), and released into space from the ISS. Fit-check was conducted by using POD from JAXA to check if our satellite can smoothly enter into POD and be deployed from POD to the space. (2022-Nov)
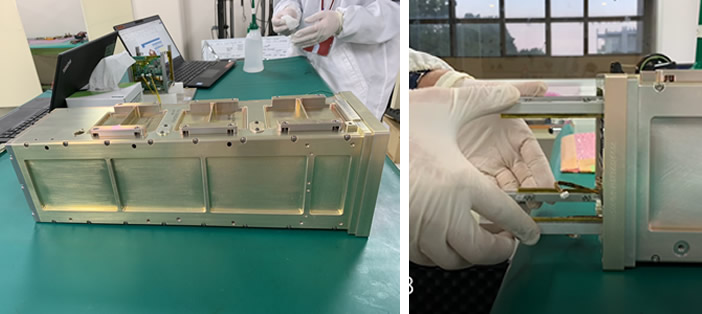
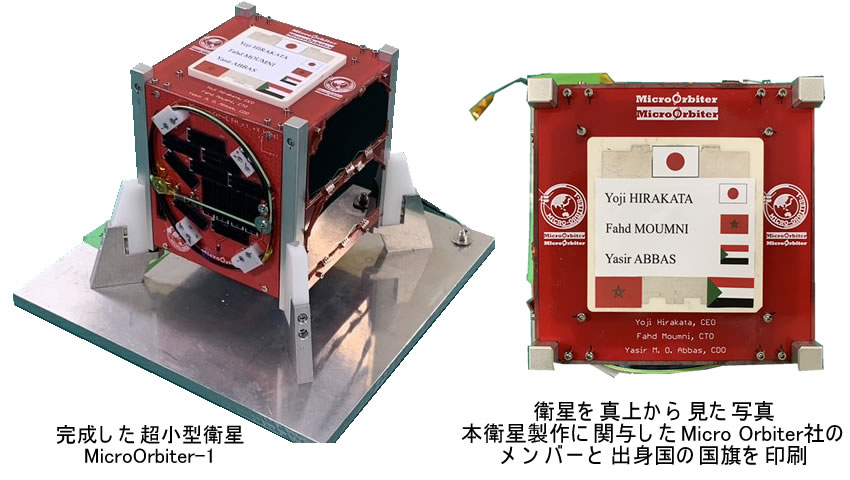
フィットチェック完了後、衛星の最終組み立てが行われ、ようやく打ち上げに使用できるフライトモデル(FM)が完成しました。衛星のトップの部分(+Z面)には平面パッチアンテナを配置していますがそのパッチアンテナ面に完成記念として当社の3名の名前と出身国国旗を印刷しています。CTO(Chief Technical Officer)のFahd Moumniはモロッコ出身、CTD(Chief Development Officer)のYasir Abbasはスーダン出身です。(2022年11月)
After the fit check was completed, the final assembly of the satellite was completed as a Flight Model (FM), which can be used for rocket launch. A flat patch antenna is placed on the top of the satellite (+Z plane), and the names of the three members of our company and the national flag of their home country are printed on the patch antenna side to commemorate the completion. CTO (Chief Technical Officer) Fahd Moumni is from Morocco and CTD (Chief Development Officer) Yasir Abbas is from Sudan. (2022-Nov)

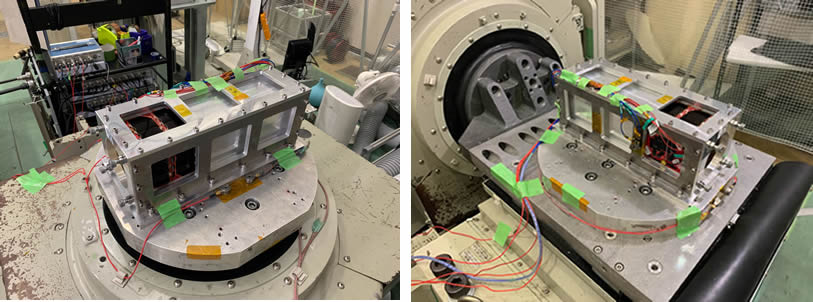
完成したフライトモデルを振動試験台の上に固定し振動解析を行った結果、各測定点における応答に許容レベルを超える変化はなく、また、ランダム振動試験前後で最低次固有振動数の周波数変化もほとんど見られず、要求された振動環境下で衛星構造に緩みや破壊が無い事を確認し振動試験は合格しました。(2022年11月)
As a result of mounting the completed flight model on the vibration test stand and conducting vibration analysis, there was no change exceeding the allowable level in the response at each measurement point, and the frequency change of the lowest natural frequency was also observed before and after the random vibration test. The vibration test passed, confirming that there was no looseness or breakage in the satellite structure under the required vibration environment. (2022-Nov)
920MHz 固定型LoRa GST (Ground Sensor Terminal) 1号機が完成。太陽光パネルで電力供給。パッチアンテナを頭頂部に設置しMicroOrbiter-1 超小型衛星にセンサーデータを送信します。
First unit of 920MHz fixed LoRa GST was completed. It is powered by solar panel. Patch antenna is installed on the top of the head to transmit sensor data to the MicroOrbiter-1 CubeSat.

JAXA納入証明書の交付がありました。米国のロケットでISSに届け、ISSの日本実験棟KiboからSatellite Orbital Deployer J-SSODを使って宇宙空間に打ち出すために、12月1日JAXAにて弊社超小型衛星がJ-SSODに精密に格納できるかの目視検査がJAXA関係者の立ち合いの下に行われ合格しました。これによりJAXAの全ての技術要求をクリアできたとして弊社衛星を正式にJAXAに受領して頂く事となり、JAXAからその証明書の交付がありました。
Our nano-satellite was stored in the J-SSOD at JAXA on December 1st in order to be delivered to the ISS by a U.S. rocket and then to be launched into space using the Satellite Orbital Deployer J-SSOD from the Japanese Experiment Module Kibo on the ISS. A visual inspection was conducted in the presence of JAXA officials, and it passed. As a result, our satellite was officially accepted by JAXA as it cleared all of JAXA’s technical requirements, and JAXA issued a certificate.


IoT超小型衛星MicroOrbiter-1の完成披露会を行いました。2024年3月18日、当社は九工大と共同研究で開発したIoT超小型衛星「MicroOrbiter-1」の完成披露会を九工大戸畑キャンパス百周年中村記念館にて開催しました。On March 18, 2024, we held an unveiling ceremony for “MicroOrbiter-1” developed through joint research and development program with Kyushu Institute of Technology at Kyushu Institute of Technology’s Tobata Campus Centennial Nakamura Memorial Hall.

IoT超小型衛星MicroOrbiter-1搭載ロケットFALCON-9は無事打ち上げられました。現地時間3月21日4:55pm(日本時間3月22日)SpaceX社のFalcon9ロケットを使用した30th Cargo Resupply Mission to ISS(SpaceX CRS-30 Cargo Dragon)はケープカナベラルから無事打ち上げられました。2日間の飛行の後、3月23日に国際宇宙ステーションにドッキングし、その後日本実験棟Kiboから当社衛星MicroOrbiter-1は地球低軌道に放出されます。
On March 21, 4:55pm local time (March 22, Japan time), the 30th Cargo Resupply Mission to ISS (SpaceX CRS-30 Cargo Dragon) using SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket was successfully launched from Cape Canaveral. After a two-day flight, it was docked at the International Space Station on March 23, and then our satellite MicroOrbiter-1 will be released into low Earth orbit from the Japanese Experiment Module Kibo.
